
As cyber threats such as ransomware and data breaches become increasingly common, protecting your data is crucial. Whether you’re a business handling sensitive customer information, a freelancer managing research files, or an individual preserving family memories, losing data can be devastating. Immutable storage provides a reliable way to keep your data secure, unchangeable, and recoverable.
What Is Immutable Storage?
Immutable storage is a data storage method in which data, once saved, cannot be changed, deleted, or overwritten for a specified period. Think of it as a digital safe: once locked, files stay untouched. Immutable storage protects against ransomware, accidental deletions, and tampering.
Using a Write Once, Read Many (WORM) model allows users to read data without altering it. Businesses use it for secure financial records, while individuals protect personal files, such as photos and documents. Available in cloud platforms like Amazon S3, enterprise drives, or backup appliances, it’s ideal for backups, archives, and compliance, ensuring tamper-proof data security.
How Does Immutable Storage Work?
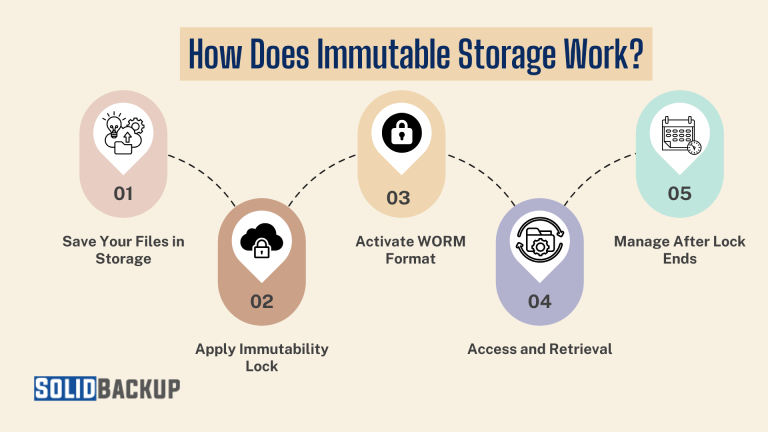
Immutable storage relies on advanced technology to lock data and maintain its integrity. The process is straightforward but highly effective, ensuring your files remain secure. Here’s a detailed look at how it functions:
- Data Storage: You save files, such as documents, videos, databases, or backups, to an immutable storage system. A cloud service, such as Microsoft Azure, a dedicated enterprise drive, or a backup appliance, can provide data storage.
- Immutability Lock: The system applies an “immutability” flag or lock, which prevents changes to the data for a specific time, such as 30 days, six months, or several years. This lock ensures that even authorised users, like system administrators, cannot edit, encrypt, or delete the data during this period.
- WORM Format: The system stores data in a Write-Once, Read-Many (WORM) format. In cloud systems, this often involves object storage, where the system saves files as unchangeable objects. On physical media, such as hard drives, the system locks files to prevent modification. This format stops ransomware from corrupting or encrypting the data.
- Access and Retrieval: You can read or retrieve the data at any time, such as restoring a backup after a cyberattack has occurred. If you need to update the data, the system creates a new version, leaving the original unchanged. This versioning ensures a clean copy is always available.
- Lock Expiration: Once the lock period ends, you can choose to delete the data, archive it, or extend the immutability for further protection.
For example, a school might store student records in an immutable cloud service with a one-year lock. If ransomware infects their systems, the locked records remain safe, allowing the school to restore them without paying a ransom. The process is automated and secure, making immutable storage user-friendly even for those without technical expertise.
Types of Immutable Storage
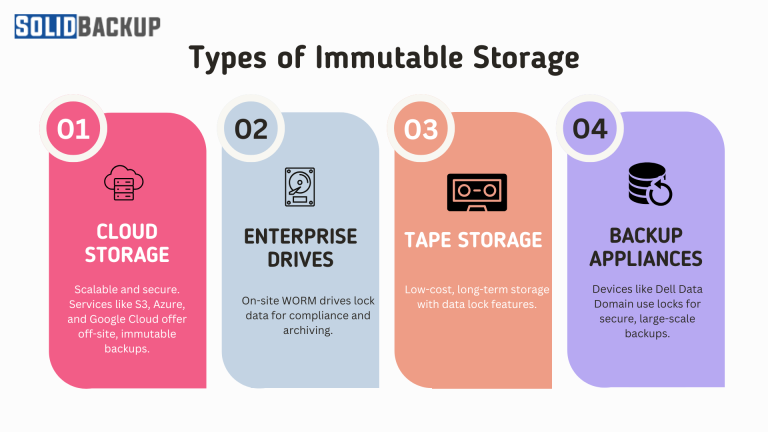
Immutable storage comes in various forms to meet different needs, offering flexibility for users:
- Cloud Storage: Services like Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud provide immutable object storage. These are scalable, secure, and ideal for off-site backups, with features like air-gapping to isolate data from networks.
- Enterprise Drives: Certain hard drives support WORM functionality, locking data for compliance or archival purposes. These are common in businesses needing on-premise solutions.
- Tape Storage: Although less popular, magnetic tape can be set as immutable, making it suitable for long-term, low-cost archiving.
- Backup Appliances: Devices like Dell’s Data Domain use retention locks to enforce immutability, offering enterprise-grade security for large datasets.
Cloud-based immutable storage is the most widely used due to its ease of access, ability to scale with data growth and advanced security features like encryption and air-gapping.
How to Start Using Immutable Storage
Setting up immutable storage is simple, even for non-tech users. Follow these steps to get started:
- Choose a Platform: Select a service like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage for cloud-based immutability, or try free trials of backup tools like Veeam for smaller setups. Check out this article to learn the difference between cloud storage vs cloud backup.
- Configure Backups: Set up your backup system to save data to immutable storage. Select a lock period (e.g., 30 days or a year) based on your specific needs, such as compliance or recovery objectives.
- Enable WORM Settings: Activate WORM or retention lock features in your storage system to make data immutable. Most platforms guide you through this process.
- Test Restores: Regularly test restoring data to ensure your immutable backups are functional and accessible when needed.
- Enhance Security: Protect access to your storage with multi-factor authentication (MFA), strong passwords, and firewalls to prevent unauthorised entry.
For optimal protection, use the 3-2-1 backup rule: keep three copies of your data on two different media (e.g., cloud and hard drive) with one off-site (e.g., immutable cloud storage). This strategy maximises security and recovery options.
Immutable Backup Security, Protection, and Prevention
Immutable backups enhance security by providing a read-only copy that no one, including authorised users, can alter or delete. They protect against:
- Ransomware: Prevent encryption or deletion of backups. Check this article to learn more about how to prevent data ransomware attacks.
- Malware: Ensure clean recovery points free from infection.
- Human Error: Stop accidental deletions or overwrites.
For maximum protection, combine immutable backups with:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Securing Access to Storage Systems.
- Zero Trust Model: Verify all users and devices accessing backups.
- Employee Training: Educate teams on phishing and cyber threats.
Why Is Immutable Storage Essential?
Immutable storage protects data by ensuring backups and files remain unchangeable and recoverable. Immutable backups prevent ransomware from compromising data, providing a clean copy for minimal downtime and eliminating the need for ransom payments. It ensures data integrity for audits and supports compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Immutable storage also enables audit trails, which are vital for industries such as healthcare and finance. For example, a business can restore records after an attack, avoiding losses while meeting legal requirements.
The Benefits of Immutable Backup
- Ransomware Resistance: Stops attackers from tampering with backups.
- Data Integrity: Ensures the preservation of accurate, unchanged files.
- Compliance: Meets regulatory retention requirements.
- Fast Recovery: Restores clean data quickly and efficiently.
- Cost Savings: Avoids ransoms and recovery expenses.
The Drawbacks of Immutable Backup
- Cost: Cloud storage for large datasets can be pricey over time.
- Inflexibility: Users can’t edit locked data, which limits the use of dynamic files.
- Physical Risks: On-premise storage is vulnerable to damage from fire or theft.
- Setup Effort: Requires initial configuration and testing.
Conclusion
Immutable storage is a straightforward yet powerful method for securing your data. Locking files to prevent changes or deletions stops ransomware, preserves data accuracy, and supports compliance. Whether you opt for cloud platforms or enterprise drives, immutable storage keeps your backups safe and ready for recovery.
Start exploring services like Amazon S3 or free trial tools to protect your personal or business data. In an era of rising cyber risks, immutable storage is the key to a secure and worry-free digital future.



