Database backup software is a specialised tool that helps organisations protect and recover critical data. The most common types of database an MSP will encounter are Microsoft SQL and MySQL.
It ensures that database data is regularly backed up and allows users to restore it in case of accidental deletion, corruption, cyber threats, or hardware failure. Businesses rely on databases for storing sensitive information, making backup software an essential component of data management strategies.
Why is Database Backup Important?
Databases hold valuable customer details, financial records, and operational data. Losing this information can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and business disruption. Database backup software provides an additional layer of protection by creating copies of data that users can restore when needed.
Databases help organisations recover quickly from unforeseen incidents such as cyberattacks, hardware failures, or human errors, ensuring smooth business operations.
How Does Database Backup Software Work?
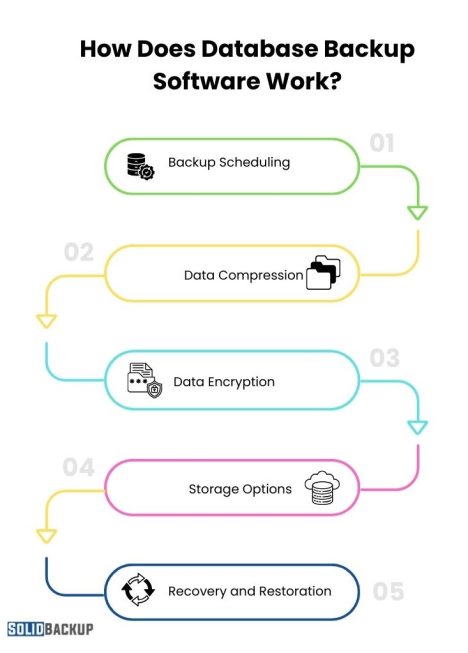
Database backup software follows a structured process to ensure it securely saves data:
Best Practices:
- Backup Scheduling – Users can schedule automatic backups at specific intervals to prevent data loss.
- Data Compression – Reduces the storage space required by compressing backup files while maintaining data integrity.
- Encryption – Ensures backup files are secure and protected from unauthorised access, reducing security risks.
- Storage Options – Backups can be stored on local drives, cloud servers, or external devices, providing multiple recovery options.
- Recovery and Restoration – Provides options to restore the database to its previous state when needed, minimising downtime.
Types of Database Backup
Different backup methods are used based on business needs and storage capacity:

01 Full Backup
A full backup creates a complete copy of the entire database. It ensures that all data is available for recovery but requires significant storage space and time. This method is ideal for businesses with smaller databases or those requiring a comprehensive backup solution.
02 Incremental Backup
An incremental backup saves only the changes made since the last backup. It is faster and requires less storage but may take longer to restore, as the system needs to combine multiple backup files. This method benefits organisations that update their data frequently but want to optimise storage usage.
03 Differential Backup
A differential backup stores all changes made since the last full backup. It requires more storage than an incremental backup but is faster to restore. Businesses that need a balance between storage efficiency and quick recovery times often choose this method.
04 Transaction Log Backup
A transaction log backup records all changes made to the database since the last backup. It helps recover data to a specific point, making it ideal for databases requiring continuous updates, such as financial or e-commerce systems.
Key Features of Database Backup Software
When choosing database backup software, consider the following features:
01 Automation
Automated backups reduce the risk of human error by ensuring the system backs up data at regular intervals without manual intervention. This feature simplifies backup management and enhances data protection.
02 Security and Encryption
Backup files should be encrypted to prevent unauthorised access. Advanced security features include end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication, ensuring data remains protected from cyber threats.
03 Scalability
As data grows, the backup solution should be able to handle increasing storage demands without affecting performance. Scalable backup software accommodates business expansion and ensures long-term usability.
04 Fast Recovery Options
A good backup solution provides multiple restoration options, allowing users to recover data quickly with minimal downtime. A fast recovery option is crucial for businesses that rely on real-time data access.
05 Storage Flexibility
Businesses should store backup data in multiple locations, including local servers, cloud storage, and external devices. Using diverse storage options enhances disaster recovery strategies.
Benefits of Using Database Backup Software
Implementing database backup software provides businesses with a reliable way to protect their data, ensuring continuity and compliance. Here are some key benefits of using backup solutions.
01 Data Protection
Backup software ensures critical business data is always safe and recoverable in case of system failure or cyberattacks. Without a backup strategy, businesses risk permanently losing valuable information.
02 Business Continuity
When data loss occurs, businesses can restore their databases quickly, minimising disruptions and ensuring smooth operations. Efficient recovery of backup data helps organisations maintain customer trust and service reliability.
03 Compliance with Regulations
Many industries require businesses to follow data protection laws. Backup solutions help meet these legal requirements by securing sensitive data and maintaining audit logs for regulatory compliance.
04 Cost Savings
Data loss can result in financial losses. Investing in reliable backup software prevents costly downtime and data recovery expenses. A proactive backup strategy reduces the risk of financial penalties due to non-compliance.
05 Ease of Use
Most backup software solutions offer user-friendly interfaces and automation, making it easy for businesses to set up and manage backups. Ease of use allows non-technical users to handle backup processes efficiently.
Challenges of Database Backup
While database backups are essential for data protection, businesses must address certain challenges to ensure reliability and security. Below are some common issues faced during backup management.
01 Storage Limitations
Large databases require significant storage space, which can be expensive. Organisations need to balance storage capacity with budget constraints when planning backup strategies.
02 Performance Impact
Frequent backups may slow down system performance, affecting business operations. Proper scheduling and optimised backup settings can minimise this impact.
03 Security Risks
Improper backup storage or weak encryption can expose sensitive data to cyber threats. Therefore, businesses should protect backup files with strong security measures.
04 Backup Corruption
If backups are not verified regularly, they may become corrupted and unusable. Regular testing and validation of backup files ensure data integrity and reliability.
Best Practices for Database Backup
Following best practices ensures that database backups remain secure, accessible, and effective in preventing data loss. Implementing these strategies helps businesses maintain smooth operations and quick recovery.
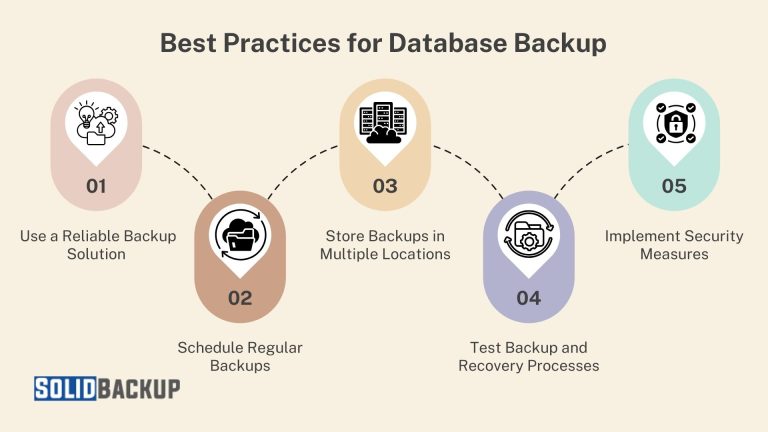
01 Use a Reliable Backup Solution
Choose software that meets your business requirements and offers robust security features. A reliable backup tool minimises the risk of data loss.
02 Schedule Regular Backups
Automate backups at regular intervals to ensure up-to-date data protection. Scheduled backups prevent gaps in backup coverage and ensure that recent data is always available.
03 Store Backups in Multiple Locations
Use cloud and on-premise storage to protect against hardware failures and cyber threats. Redundant storage locations enhance disaster recovery preparedness.
04 Test Backup and Recovery Processes
Verify backup files regularly and test the restoration process to ensure backups work correctly. This practice prevents unexpected failures during data recovery.
05 Implement Security Measures
Encryption, strong passwords, and access controls protect backup files from unauthorised access. Regular security audits enhance backup file protection.
A well-planned backup strategy ensures data security and quick recovery. Implementing a backup retention policy helps manage storage, while data backup versioning ensures access to previous copies when needed. Combining these with automation, encryption, and regular testing enhances backup reliability.
Conclusion
Database backup software is essential for protecting critical business data and ensuring quick recovery in case of data loss. Businesses can safeguard their information, maintain continuity, and prevent costly downtime by choosing the right solution, automating backups, and following best practices. A robust backup strategy is wise for any organisation relying on digital data.



