Cloud backup refers to copying your files, folders, or entire systems to remote servers through the Internet. It helps protect your data from hardware failure, accidental deletion, theft, or natural disasters. Unlike traditional backups stored on physical drives, cloud backup stores your data off-site in secure, professionally managed data centres.
We will examine cloud backup, its benefits, potential problems, and advantages. It keeps data safe and easy to retrieve, no matter what happens.
Understanding Cloud Backup
Cloud backup means copying data from your devices—such as computers, smartphones, or servers—to remote servers managed by a third-party provider. These servers, housed in secure data centres, are designed to withstand physical and cyber threats, protecting your data against disasters like fires, floods, or hardware failures. The “cloud” refers to this network of remote servers, which you access over the internet, eliminating the need for on-site storage hardware.
Cloud backup is distinct from other cloud services like file-sharing platforms (e.g., Google Drive or Dropbox), as it prioritises data protection over collaboration. While file-sharing services allow you to store and sync files for easy access, cloud backup focuses on creating secure, redundant copies of your data to restore in case of loss. Providers like Backblaze, Carbonite, iDrive, and Acronis specialise in backup solutions, offering tools to automate and streamline the process.
How Does Cloud Backup Work?
The cloud backup process is user-friendly and typically involves the following steps:
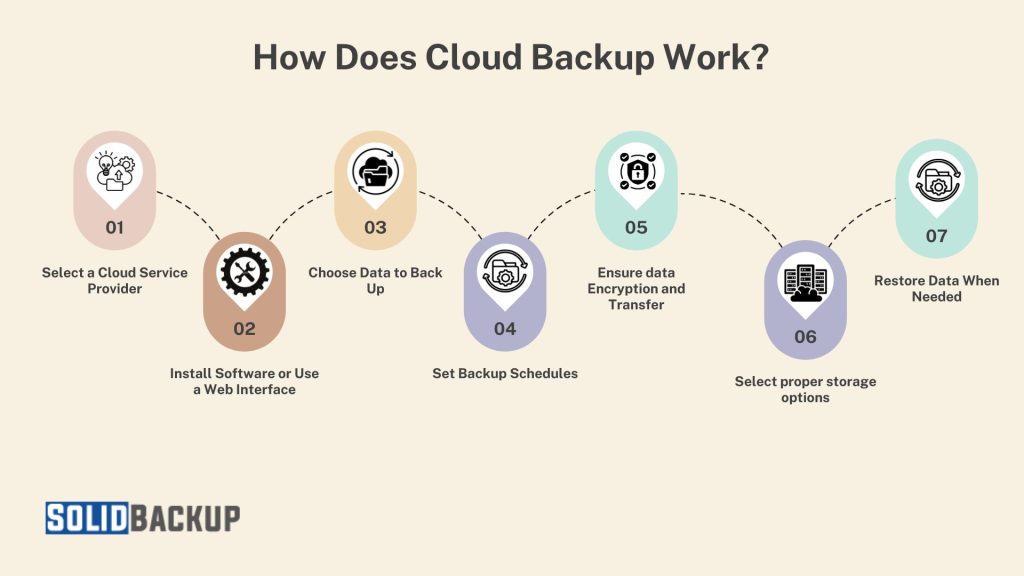
1. Select a Provider: Choose a reputable cloud backup service that meets your needs, including storage capacity, security features, and budget. Popular options include Google One, Microsoft OneDrive, Backblaze, and Carbonite.
2. Install Software or Use a Web Interface: Most providers offer dedicated apps for desktops and mobile devices, as well as browser-based dashboards, to manage backups.
3. Choose Data to Back Up: You can select specific files, folders, or systems for backup. Many services allow you to prioritise critical data, such as work documents or family photos.
4. Set Backup Schedules: Configure backups to run automatically in real-time as files change or at scheduled intervals (e.g., daily or weekly). This automation reduces the risk of forgetting to back up important data.
5. Data Encryption and Transfer: Files are encrypted before leaving your device, ensuring they remain secure during transfer and storage. Providers use protocols like AES-256 encryption to protect against unauthorised access.
6. Storage on Remote Servers: Your data is stored in multiple data centres, often across different geographic locations, to ensure redundancy and availability.
7. Restore Data When Needed: If hardware failure, ransomware, or accidental deletion causes data loss, you can log into your account to download specific files or restore entire systems.
This seamless process makes cloud backup accessible to non-technical users while offering robust features for businesses with complex needs.
Benefits of Cloud Backup
Cloud backup offers a range of advantages that make it a preferred choice for data protection:

- Accessibility: With an internet connection, you can access your backed-up data from any device, anywhere in the world. Cloud Backup is ideal for remote workers, travellers, or anyone needing to retrieve files on the go.
- Scalability: Cloud storage is flexible, allowing you to increase or decrease capacity as your needs evolve. Unlike physical drives, there’s no need to purchase new hardware.
- Automation: Automated backups eliminate the need for manual intervention, ensuring your system consistently protects your data with minimal effort.
- Disaster Recovery: Since data is stored off-site, it is safe from local disasters such as fires, floods, or theft. Disaster recovery makes cloud backup a cornerstone of robust disaster recovery plans.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Subscription-based pricing spreads costs over time, avoiding the upfront expense of physical storage devices. Many providers offer affordable plans for individuals and businesses.
- Versioning: Many cloud backup services retain multiple versions of files, allowing you to recover older iterations if you accidentally overwrite or delete data.
- Security: Leading providers use military-grade encryption and comply with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, which helps protect your data from cyber threats.
Challenges of Cloud Backup
Despite its strengths, cloud backup has some limitations to consider:
- Internet Dependency: Backups and restores require a stable internet connection. Cloud backup can be a significant hurdle in areas with slow or unreliable connectivity.
- Privacy Concerns: Storing data with a third party raises questions about who owns or can access your files. While reputable providers use strong encryption, choosing a trustworthy service is critical.
- Ongoing Costs: Unlike one-time purchases of external drives, cloud backup subscriptions involve recurring fees, which can accumulate over time.
- Initial Backup Time: Uploading large datasets, such as terabytes of media files, can take days or weeks, depending on your internet speed. However, subsequent incremental backups, which only upload changes, are much faster than the initial full backup.
- Data Recovery Speed: Restoring large amounts of data from the cloud can be time-consuming, especially compared to local backups.
- Service Reliability: Accessing your data could become challenging if a provider goes out of business or experiences outages. Researching a provider’s reputation and redundancy measures is essential.
Cloud Backup vs. Other Backup Methods
To appreciate cloud backup’s unique value, it’s worth comparing it to other methods:
- Local Backups: External hard drives or USB sticks are affordable and fast for local restores, but are vulnerable to physical damage, theft, or loss. They also require manual updates and lack remote access.
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): NAS devices provide local networked storage with some automation, but they require technical setup, maintenance, and protection against on-site risks.
- On-premises servers: Large organisations may use dedicated servers for backups, which provide control but require a significant investment in hardware, power, and IT expertise.
- Hybrid Backups: Some users combine cloud and local backups for the best of both worlds—local speed and off-site security. For example, you might back up critical files to a hard drive and the cloud.
Cloud backup excels in ease of use, off-site protection, and minimal maintenance, making it ideal for individuals, small businesses, and enterprises that seek reliable data protection without complex infrastructure.
Who Should Use Cloud Backup?
Cloud backup is versatile and suits a wide range of users:
- Individuals: Protect personal files, such as photos, videos, and documents, from device failures or accidental deletion. Services like Google One or iCloud are popular for personal use.
- Small Businesses: Secure business-critical data, such as customer records or financial documents, without investing in expensive servers. Providers like Backblaze and Carbonite cater to the needs of small businesses.
- Remote Workers: Ensure work files are backed up and accessible across multiple locations, supporting flexible work arrangements.
- Enterprises: Use scalable backup solutions to manage large amounts of data and meet compliance standards for industries like healthcare and finance.
- Creative Professionals: Photographers, videographers, and designers can safeguard large media files, leveraging the cloud’s scalability to store terabytes of content.
Choosing the Right Cloud Backup Service
Selecting a provider requires careful consideration of your needs:
- Storage Capacity: Assess how much data you need to back up now and in the future. Some providers offer unlimited storage, while others have tiered plans.
- Security Features: Look for end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Ease of Use: A simple interface and setup process are crucial, especially for non-technical users.
- Customer Support: 24/7 chat, email, or phone support can be a lifesaver during data recovery.
- Pricing: Compare plans to find a balance between cost and the features you need. Some providers offer free tiers with limited storage, which is ideal for testing.
- Additional Features: Look for versioning, file-sharing capabilities, or integration with other tools (e.g., Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace).
Best Practices for Cloud Backup
To maximise the benefits of cloud backup:
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Keep three copies of your data (one primary, two backups), store them on two different types of media, and keep one copy off-site, such as in the cloud.
- Test Restores: Periodically verify that you can restore files to ensure your backups are functional.
- Monitor Storage Usage: Regularly check your storage limits to avoid unexpected fees or interruptions.
- Secure Your Account: Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication to protect your backup account.
- Combine with Local Backups: For critical data, maintain a local copy alongside your cloud backup for faster recovery.
Conclusion
Cloud backup is one of the most efficient and secure ways to protect your data. Whether you’re an individual saving personal files or a business protecting critical systems, cloud backup offers flexibility, automation, and peace of mind. Choose a reliable cloud backup service, set up regular backups, and ensure your data stays safe, no matter what happens to your local device.



