Data is one of the most valuable assets for individuals and businesses. Losing data due to accidental deletion, hardware failure, or cyberattacks can cause significant disruptions. Backups help protect essential files, and one efficient method is incremental backup. Users prefer this method due to its speed and minimal storage requirements.
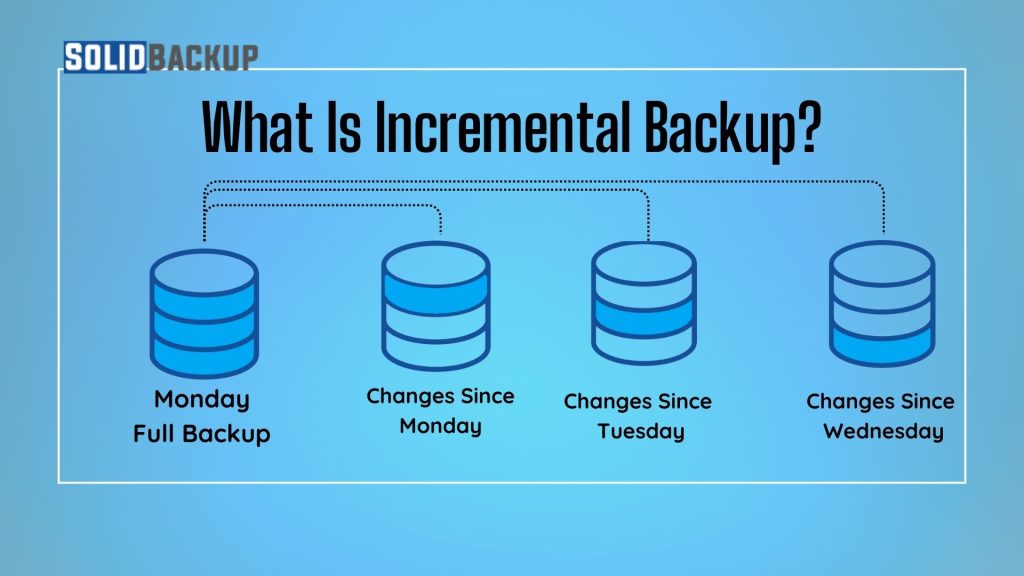
Understanding Incremental Backup
An incremental backup is a type of backup that only saves the changes made since the last backup. Instead of copying all data every time, it captures only modified or newly added files, making the process faster and saving storage space.
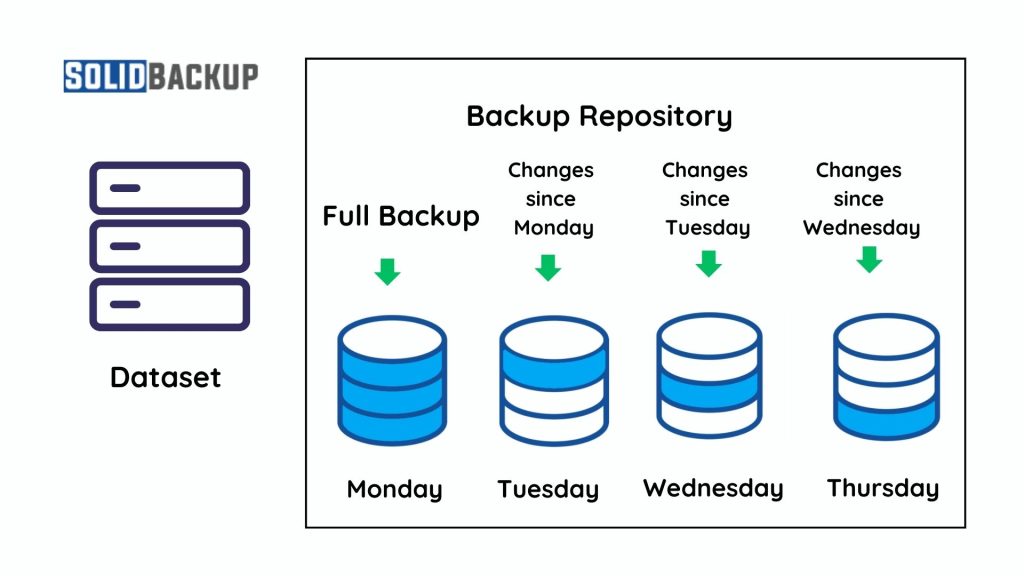
For example, if users perform a full backup on Monday, an incremental backup on Tuesday will store only the changes since Monday. A backup on Wednesday will save only the changes since Tuesday, and so on.
How Incremental Backup Works
Incremental backups follow a structured process:
- Full Backup (Initial Step) – The first backup is a complete copy of all data.
- Incremental Backups (Ongoing Steps) – Each subsequent backup only includes files that have changed since the last backup.
- Restoration Process – The system uses the full and incremental backups to restore data.
Benefits of Incremental Backup
Incremental backup offers several advantages:
01. Faster Backup Process
Since only modified files are stored, incremental backups take significantly less time than full backups. This efficiency makes incremental backups ideal for frequent backups without disrupting system performance.
02. Reduced Storage Requirements
Incremental backups use less storage space by backing up files that have changed since the last backup, making them ideal for cloud-based storage or systems with limited capacity.
03. Lower Bandwidth Usage
Incremental backups reduce network strain by transferring only the necessary data, which is especially useful for businesses and individuals relying on cloud backups or working with remote servers.
4. Efficient Data Management
Incremental backups allow businesses to maintain regular and efficient data protection without overloading their systems. The ability to schedule frequent backups enhances disaster recovery plans.
Drawbacks of Incremental Backup
Despite its advantages, incremental backup has some limitations:
01. Longer Restoration Time
Restoring data requires retrieving the full backup and all incremental backups in sequence, which can take significantly longer than restoring from a single full backup.
02. Higher Risk of Data Loss
If any incremental backup file is missing or corrupted, restoring data can become complicated, making managing and verifying backup integrity crucial.
03. Complex Management
Managing multiple incremental backups requires careful monitoring and organisation. Businesses need a structured backup plan to ensure consistency and reliability.
Incremental Backup vs. Other Backup Types
Understanding how incremental backup compares to other backup methods helps in choosing the right solution:
| Backup Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Copies all data every time | Easy restoration | Takes time and storage |
| Incremental Backup | Saves only changed files since last backup | Fast, low storage use | Slow restoration |
| Differential Backup | Saves changes since the last full backup | Faster than full backup | More storage than incremental |
| Mirror Backup | Creates an exact copy | Immediate access | Risky if accidental deletion occurs |
Best Practices for Incremental Backup
To ensure incremental backups are reliable, follow these best practices:
1. Automate Backups
People often forget manual backups, increasing the risk of data loss. Automating incremental backups ensures consistency, eliminates human error, and runs on a set schedule. It reduces workload while providing logs and notifications for monitoring. This approach guarantees reliable data protection without requiring manual intervention.
2. Use Hybrid Backup Strategies
Combining incremental backups with full or differential backups balances speed, storage efficiency, and restoration time. Many organisations use a mix of backup types for optimal results.
3. Encrypt Backup Data
Security is essential, especially for sensitive files. Encrypting backup data prevents unauthorised access and ensures privacy even if the backup is compromised.
4. Test Backups Regularly
A backup is only valid if the system successfully restores it. Regular testing ensures data is recoverable and identifies potential issues before failure occurs.
5. Store Backups in Multiple Locations
Keeping backups in different locations, such as an external hard drive and cloud storage, protects against data loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
Conclusion
Incremental backup is an efficient method for data protection, reducing storage use and speeding up the backup process. While it has some drawbacks, following best practices can help businesses and individuals maintain reliable data backups. Choosing the correct backup method depends on factors such as backup speed, storage limitations, and ease of restoration.



