Schools, Universities, and other Educational facilities increasingly appear to be easy targets for cybercriminals, primarily through ransomware attacks.
School Sysadmins need to know what ransomware is, how it operates, and, most importantly, how to prevent it so their data is safe and their operations are not compromised.
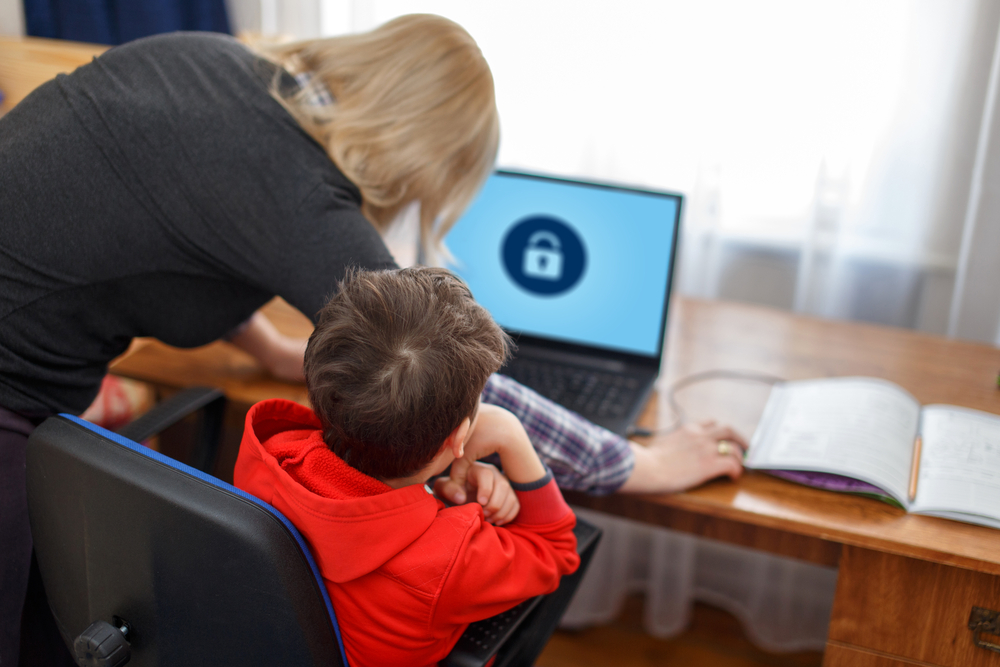


What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a form of malware designed to encrypt the victim’s digital content files and prevent access to their information.
Ransomware holds these files for ransom, making the individual pay the demanded amount to access the key for decryption.
School operations could be shut down, possibly locking administrative records, student information, academic materials, and other critical infrastructural systems.
The Stages through Which a Ransomware Attack Unfolds
Stage 1: Weapon Delivery. Method: Ransomware may come in several forms, each with its distinct approach to delivery
Phishing emails
These look like genuine emails, often spoofed from respected sources, but their objective is to dupe end-users into clicking on attachments or links that can download and install ransomware.
Malicious sites
Clicking on malicious links, such as those posted on various sites or social media or viewing compromised websites might lead to ransomware downloads without the person knowing about it.
No security measures in the software
The system might get infected through the vulnerabilities present in the unpatched or outdated software, allowing an access point for ransomware to intrude.
Removable media
Ransomware is easily installed throughout the network through personal USB or external hard drives. Traditionally not considered critical attack surfaces, downloaded files may have originated from untrusted sources.
Stage 2: After infiltration, Ransomware works in the background, where it only monitors valuable data files
The Ransom Demand: Ransomware uses strong encryption algorithms to encrypt your files, blocking all access until a ransom is paid.
After data encryption, ransomware usually delivers a message to the affected device at the current workstation, informing the user that they are a victim and asking for a ransom to regain access to the files.
These messages may be urgent to the victim, reminding them they should pay quickly to get a discount or threatening the permanent deletion of encrypted data.
Limited cybersecurity resources: It is worth noting that schools usually have minimal budgets; this means there can always be more investment in cybersecurity infrastructure and hiring a fully funded IT team.

How to Stop the Cybercriminals
Infrastructure vulnerability: Of course, the first step is to prevent cybercriminals from getting into your network, either directly or by proxy. School networks often have vulnerable software, legacy systems, and minimal tech staff and budgets, which are inviting for any cybercriminal.
This isn’t what we do. Instead, our partners will supply the tech know-how, systems and processes to make the network as secure as possible. Our sole task is to provide a Solid Cloud backup solution that can be used to restore critical data after an attack.
A simple backup fixes all this: You can start with a 100GB Free lifetime backup account and cloud storage from us today.
Pressure to restore operations quickly: Schools face enormous pressure to rapidly restore operations and access to essential data to avoid prolonged disruption for teachers and students.
These can, under pressure, make the schools consider paying the ransom even if they are not advised to.
When your data is backed up, you can restore it confidently and avoid engaging with cybercriminals.

What can be done to Prevent Ransomware in Schools
To minimise the risk of ransomware, schools should consider the following measures:
User education and awareness: The staff and students need to undergo training on the guidelines for identifying unknown emails, links, and attachments and reporting suspicious activities.
Educate all students through workshops, distributing informational materials and the curriculum, and working with the cybersecurity principle to develop a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
Secured IT Infrastructure: To achieve this, there is a need for an active and robust infrastructure that sees a leader with strong support of patching towards maintaining their supported software and operating systems. This ensures they receive current and updated security patches.
Block potential threats with security software, such as antivirus, anti-malware, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
Segment the network so that sensitive data can be isolated; therefore, the damage can be minimised if an attack occurs.
Strong implementation to authenticate the protocols and complexity implemented on password policies to avoid unauthorised access.

Backups and Recovery
Putting everything back together again
Regularly back up essential data to secure offline storage locations so that the data is isolated from the network and not accessible by the ransomware.
Testing the recovery process as often as possible is as simple as 1-2-3. It is necessary to ascertain your ability to efficiently restore your data following ransomware attacks and other disaster recovery causes, such as hardware and software failure and employee deletion.

Incident Response Plan
Prepare a comprehensive incident response plan defining all the steps during a ransomware attack.
This will define roles and responsibilities, communication strategies, and procedures for notifying authorities.
The plan should be reviewed and updated when necessary to maintain effectiveness.
Never encourage ransom payment. This only rewards criminal activity and does not guarantee the recovery of your data.
The victim must report the ransomware attack to local law enforcement agencies so that they can investigate and track the bad actors’ activities.

Unlimited History & Retention
Keep as many versions of all your files as you want.
Backup Windows & macOS
Backup other LAN devices using UNC paths.
Backup external drives and NAS
Backup external disks and drives, &NAS devices.
100% Private Encryption
No one can read your data apart from you (not even us).
Conclusion
Combating ransomware will require a proactive stance, a multi-layer defence system, and a culture of cybersecurity awareness. This will put your school in a better position to prevent and recover from any cyber attack.
Ransomware prevention is not an alternative; it’s necessary for a secure learning environment.


