Every computer needs a way to keep data safe for the future. That’s where secondary storage comes in. Unlike your computer’s short-term memory, which forgets everything when you switch off, secondary storage holds onto your files, photos, and more. Whether saving holiday snaps or running a business, secondary storage is a game-changer. Let’s explore what it is, why it matters, and how it helps you daily.
What is the Definition of the Term' Secondary Storage' ?
Secondary storage is a part of a computer system that stores data for an extended period. It keeps your files safe, even when your device is powered off. Consider it a digital locker for your documents, music, and videos. Unlike primary storage, such as RAM, which only holds data while your computer is running, secondary storage is non-volatile. It doesn’t forget anything, making it perfect for saving things you’ll need later.
Secondary storage comes in many forms, from hard drives to USB sticks. Manufacturers design it to handle all kinds of tasks, whether you’re a student saving homework or a company storing customer records. By offering a reliable way to keep data, secondary storage ensures you can always access essential files.
What is Stored in Storage Devices?
Secondary storage holds just about anything you want to keep. It saves personal files like photos from your last holiday, favourite songs, or essays for school. It also stores apps, games, and the software that makes your computer work. For businesses, secondary storage is a treasure chest for customer details, sales reports, employee records, and project plans.
In short, secondary storage is where you put anything you don’t want to lose. It acts like a digital filing cabinet, keeping everything organised and ready for when needed. Whether it’s a single photo or a massive database, secondary storage has the space to handle it.
Why Do Computers Need Secondary Storage?
Computers need secondary storage to save data permanently. Without it, everything would vanish the moment you turn off your device. Primary storage, such as RAM, is excellent for quick tasks—it helps your computer run apps and open files quickly. But it’s temporary, and he forgets everything when the power goes off.
Secondary storage solves this problem by providing a place to store files, so you can pick up where you left off. It lets you share data between devices, like moving a presentation to a colleague’s laptop. Plus, it’s essential for backups, ensuring your data stays safe from accidents or technical glitches. Without secondary storage, computers would be far less practical.
What is the Purpose of Secondary Storage?
Secondary storage has several big jobs that make it super important:
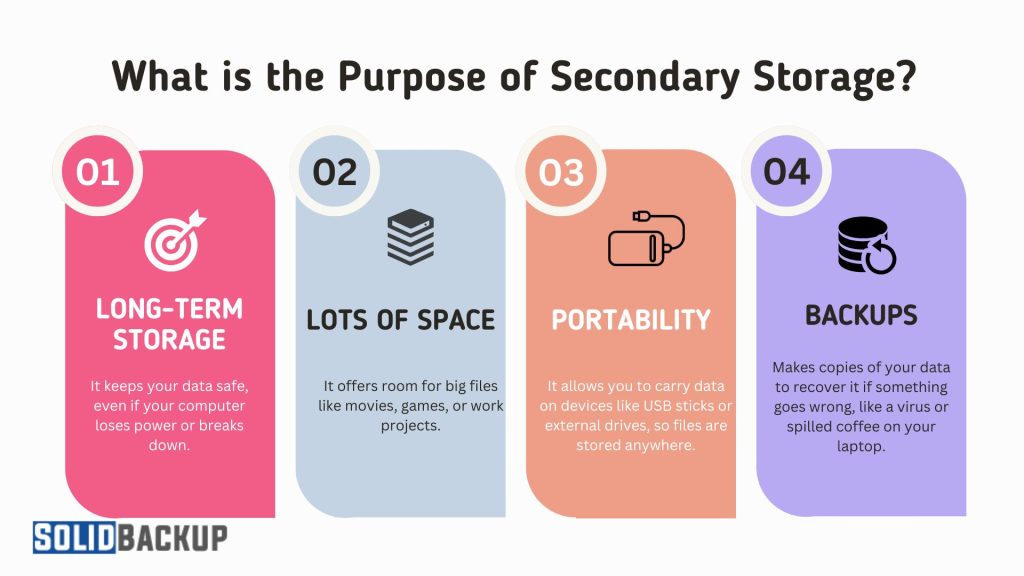
- Long-Term Storage: It keeps your data safe, even if your computer loses power or breaks down.
- Lots of Space: It offers room for big files like movies, games, or work projects.
- Portability: It allows you to carry data on devices like USB sticks or external drives, so files are stored anywhere.
- Backups: They help you make copies of your data to recover it if something goes wrong, like a virus or a spilt coffee on your laptop.
Secondary storage handles these tasks, keeping your digital life organised and secure. It’s like a trusty sidekick for your computer.
Examples of Secondary Storage Devices
You’ve probably used secondary storage devices without even thinking about it! Here’s a rundown of the most common ones:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): These use spinning disks to store vast data. They’re affordable and common in desktops and laptops.
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs): These are faster and more durable, using flash memory. You’ll see them in newer, speedier computers.
- USB Flash Drives are small and portable, so they’re great for moving files between devices, like sharing a video with a friend.
- Memory Cards: Phones, cameras, and gaming consoles use these to save photos, videos, or game progress.
- Optical Discs: CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs store music, films, or software, though they’re less common now.
- External Hard Drives: These plug into your computer via USB and hold massive amounts of data, perfect for backups.
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): These are shared drives connected to a network so that multiple people can access files from different devices.
Each device has perks, like speed, size, or portability, so that you can pick the best.
Can RAM be Used for Secondary Storage?
No way—RAM can’t act as secondary storage. RAM, or Random Access Memory, is your computer’s short-term memory. It stores data while you’re working, such as browsing the web or playing a game. But when you turn off your computer, RAM forgets everything.
Secondary storage, on the other hand, keeps data safe forever (or until you delete it). Manufacturers design RAM for long-term use, not quick tasks. RAM works at super-fast speeds, which makes it ideal for running apps, but manufacturers do not create it to save files permanently. That’s why devices need secondary storage to keep data secure.
Cloud-based Secondary Storage
Cloud storage is a modern take on secondary storage. Instead of saving files on a physical device, you store them online using services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or Microsoft OneDrive. You can access your files from any device—your phone, laptop, or even a friend’s computer—as long as you’ve got Wi-Fi.
Cloud storage is fantastic for a few reasons:
- Flexibility: You can add more space without buying new hardware.
- Sharing: It’s easy to send files to others or work on projects together.
- Safety: Your data is stored off-site, so it’s safe from things like fires or theft.
However, you need an internet connection to access your files, and you should use strong passwords to keep your data private. Cloud storage is a handy option for anyone who wants convenience and accessibility.
Key Differences Between Primary and Secondary Storage
Primary and secondary storage are like two sides of a coin—they work together but do different jobs. Here’s how they stack up:
| Feature | Primary Storage | Secondary Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Retention | Loses data when power is off (e.g., RAM). | Keeps data safe forever, even without power. |
| Speed | Very fast, runs apps smoothly. | Slower, designed for long-term storage. |
| Space | Smaller, holds less data. | Much larger, stores gigabytes or terabytes. |
| Cost | More expensive per unit of storage. | Cheaper for storing large amounts of data. |
| Job | Handles active tasks, like running a browser. | Saves files for later use. |
Both types are essential, but secondary storage keeps data safe for the long haul.
How Does Secondary Storage Support Data Backup and Recovery?
Secondary storage is your safety net for Data Backup and Recovery. It lets you make copies of your files to protect them from disasters, like a broken computer, a virus, or accidentally deleting something important. For example, you can save backups on an external hard drive or a network-attached storage (NAS) device. These copies ensure you can restore your files if something goes wrong.
Cloud storage is another great backup option. It keeps your data safe on remote servers, so your files remain there even if your house floods or your laptop gets stolen. Regular backups also mean you can quickly recover photos, work documents, or business records, saving you from stress and loss.
Businesses mainly rely on backups. They use secondary storage to save critical data, such as customer orders or financial records, so they can get back to work quickly after a problem. Whether it’s a USB drive or a cloud service, secondary storage makes recovery reliable and straightforward.
Why Businesses Rely on Secondary Storage for Long-Term Data Retention
Businesses need secondary storage to keep their data safe for years. They save all sorts of things, like customer contact information, sales reports, contracts, and employee files. Sometimes, laws require them to keep these records for a long time, like for tax audits or legal reasons.
Secondary storage devices, like SSDs or NAS systems, offer large amounts of space at a low cost. Secondary storage makes them perfect for storing vast amounts of data without incurring high costs. They also make it easy to find old files when needed, like pulling up a client’s history or checking past projects.
Plus, secondary storage is scalable. As a business grows and collects more data, it can add more storage without much hassle. This flexibility ensures that companies can keep up with their data needs, making secondary storage a vital tool for long-term success.
The Role of Secondary Storage in Business Continuity
Business continuity is about keeping a company running, even when things go wrong, such as a power outage, a cyberattack, or a storm damaging the office. Secondary storage plays a considerable role in protecting critical data. Businesses use it to back up files, allowing for quick recovery if a computer crashes or gets hacked.
For example, a NAS device can store backups of customer orders and financial records. If a server fails, the business can restore the data and keep working. Cloud storage takes it further by keeping backups off-site, safe from physical damage like fires or floods.
By having extra copies of data, secondary storage helps businesses avoid downtime, which can cost money and upset customers. It ensures they can return to normal fast, keeping operations smooth and clients happy.
Conclusion
Secondary storage is like your computer’s trusty memory, keeping your data safe and ready whenever you need it. It saves everything from family photos to business records, makes backups a breeze, and lets you carry files anywhere. With devices like hard drives, SSDs, USB sticks, and cloud storage, it fits every need, whether you’re a student or a company boss.
For businesses, secondary storage is a lifeline that supports long-term data storage and helps them recover from disasters. As technology improves, secondary storage will get even faster, bigger, and more secure. Ensuring your data is always there when needed is essential to our digital world.



