
Managing data is a big part of our lives in today’s digital world. We’re creating more files than ever, from family photos and videos to work documents and business records. However, storing all this data can be expensive and take up much space, whether on your computer, an external drive, or a cloud service.
One simple solution to tackle this problem is file compression. Compressing files shrinks their size, saving space and cutting storage costs. You will learn how file compression works and why it’s a game-changer for reducing storage needs.
What is File Compression?
File compression reduces the size of files, making them take up less space on your device or storage service. It removes unnecessary data or reorganises the file’s structure to store the same information more efficiently.
Think of it like packing a suitcase: compression squeezes your files into a smaller “package” without losing the contents. Once compressed, you can unzip or decompress the files to use them again.
Compression will be beneficial as data sizes grow with high-resolution photos, 4K videos, and complex software. By shrinking files, you can save storage space, reduce costs, and make it easier to manage your data.
Whether you’re a student, professional, or business owner, compression is a practical way to keep your storage under control.
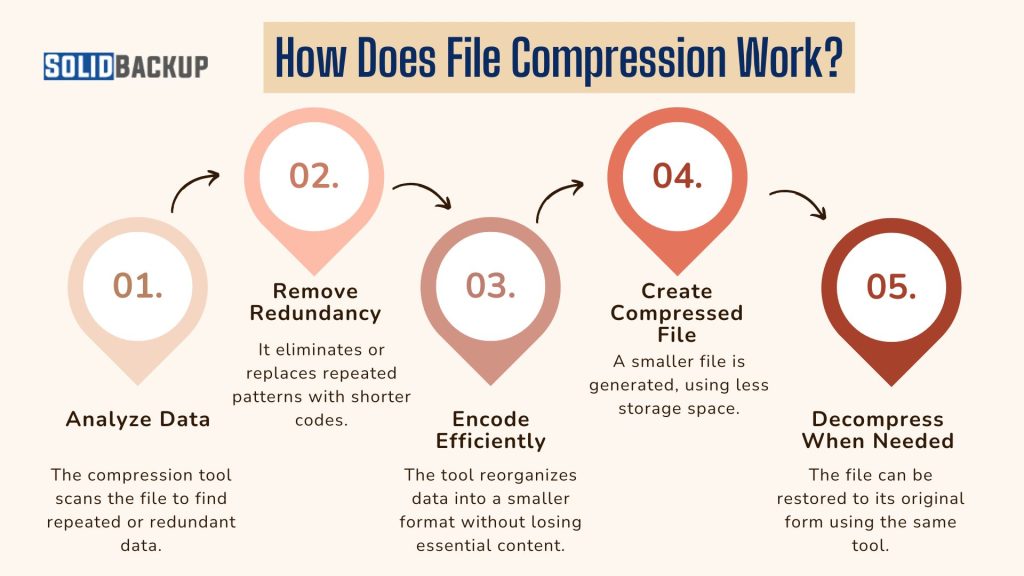
How Does File Compression Work?
Compression uses special software or tools to make files smaller. There are two main types of compression:
- Lossless Compression: Shrinks files without losing data. When you decompress the file, it’s identical to the original. Standard formats for images include ZIP, RAR, and PNG. Lossless compression method is perfect for documents, spreadsheets, or photos where every detail matters.
- Lossy Compression: It reduces file size by removing some data, like less noticeable parts of an image or video. The decompressed file isn’t the same, but often looks or sounds good enough. Formats like JPEG for images or MP3 for audio use lossy compression. It’s great for media files where perfect quality isn’t critical.
Here’s a simple example: A 10MB photo might compress to 2MB as a JPEG (lossy) or 5MB as a PNG (lossless). The JPEG is smaller but might lose some detail, while the PNG keeps everything but takes more space.
Compression tools analyse the file’s data, remove redundancies (like repeated patterns), and pack the information tightly. You can compress single files, folders, or multiple files into one archive (e.g., a ZIP file). In 2025, tools like WinZip, 7-Zip, and built-in features on Windows and macOS make compression quick and user-friendly.
Why Compress Files? Benefits of Storage Costs and Sizes
Compressing files offers several advantages, especially when saving space and money. Here are the key benefits:
1. Saves Storage Space
- Personal Devices: Laptops or phones with limited storage benefit from smaller files, letting you store more without upgrading.
- External Drives: Fit more data on USB sticks or external hard drives, delaying the need for new purchases.
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive or Dropbox charge based on the storage used. Compressing files reduces your usage, keeping you within free tiers or cheaper plans.
2. Cuts Storage Costs
Storage isn’t free, especially for cloud services or large-scale business needs. Compression helps you save money by:
- Reducing Cloud Costs: If you’re paying £7.99/month for 2TB on Google One, compressing files might let you downgrade to a 200GB plan for £2.49/month, saving £66/year.
- Delaying Hardware Upgrades: Instead of buying a new 1TB drive for £50, compress files to fit on your existing 500GB drive.
- Business Savings: Companies with massive data (e.g., video production or databases) can compress files to lower server or cloud costs, potentially saving thousands annually.
3. Speeds Up File Transfers
Compressed files are smaller, so they upload or download faster and save time when:
- Sharing Files: Emailing a 10MB ZIP file is quicker than a 50MB folder, especially with slow internet.
- Cloud Backups: Smaller files upload faster to services like Backblaze, reducing backup times.
- Moving Data: Transfer compressed files to external drives or between devices more quickly.
4. Organises Data
Compression lets you bundle multiple files into one archive, making managing it easier. For example, compressing 100 photos into one ZIP file keeps your storage tidy and simplifies sharing or backing up.
5. Enhances Backup Efficiency
Smaller files mean faster and cheaper backups. Whether using cloud backup (like IDrive) or local drives, compression reduces the storage and bandwidth needed, making your backup process smoother and more cost-effective.
How Compression Reduces Storage Costs in Practice
Let’s look at real-world scenarios in 2025 to see how compression saves money and space:
- Personal Use: You have 50GB of photos and videos on Google Drive, nearing the 15GB free limit. Compressing them to 30GB keeps you under the limit, avoiding a £2.49/month plan (£29.88/year savings).
- Small Business: A graphic designer stores 500GB of project files on Dropbox (2TB plan, £9.99/month). Compressing files to 300GB allows downgrading to a 1TB plan (£7.99/month), saving £24/year.
- Enterprise: A video production company uses 10TB on a cloud server (£500/month). Compressing files to 6TB reduces costs to £300/month, saving £2400/year.
These examples show how compression directly lowers storage needs, letting you stick with cheaper plans or smaller hardware.
Tools for File Compression
In 2025, compressing files is easier than ever with user-friendly tools. Here are popular options:
- WinZip: A paid tool with a simple interface for creating ZIP files; great for beginners.
- 7-Zip: Free, open-source software supporting multiple formats (ZIP, RAR); ideal for advanced users.
- Windows/macOS Built-In Tools: Right-click files on Windows to “Send to Compressed (zipped) Folder” or use macos’s “Compress“ option.
- Cloud Services: Some cloud platforms, like Google Drive, compress files automatically when downloading multiple items.
- Specialised Apps: Tools like HandBrake (for videos) or TinyPNG (for images) optimise specific file types.
Most tools let you choose compression levels (e.g., maximum for smallest size) and password-protect archives for security.
Tips for Effective File Compression
To maximise savings and efficiency, follow these tips:
- Choose the Right Format: Use lossless compression (ZIP, PNG) for documents or photos needing full quality; use lossy (JPEG, MP3) for media where slight quality loss is okay.
- Compress Regularly: Make compression part of your workflow, especially for large files like videos or project folders.
- Test Decompression: Unzip files occasionally to ensure they’re intact and usable.
- Combine with Cloud Backup: Compress files before backing up to services like IDrive to save space and speed up uploads. For more on cloud backup, read our article What is Cloud Backup?.
- Organise Archives: Name ZIP files clearly (e.g., “2025_Photos.zip”) so you can find them easily later.
- Monitor Storage: Check your storage usage monthly to see how compression reduces your needs.
Potential Downsides of Compression
While compression is powerful, it has a few limitations:
- Time-Consuming: Compressing large files, like 4K videos, can take minutes or hours, depending on your device.
- Quality Loss (Lossy): Lossy compression (e.g., JPEG) may reduce image or video quality, so use it wisely.
- Decompression Needed: You must unzip files to use them, which can be a minor hassle.
- Not All Files Compress Well: Some files, like already-compressed MP3s or PDFs, don’t shrink much further.
Despite these drawbacks, the space and cost savings often outweigh the inconveniences, especially for large datasets.
Why Compression Matters in 2025
With data creation skyrocketing—think 8K videos, AI-generated content, and massive business databases—storage costs are a growing concern. Cloud providers charge more for higher tiers, and hardware upgrades are pricey. Compression is a budget-friendly way to stretch your existing storage, whether a 256GB phone or a 10TB cloud plan. Plus, with faster internet and more innovative compression tools in 2025, it’s quicker and more effective than ever.
Conclusion
Compressing files is a simple yet powerful way to reduce storage costs and sizes in 2025. By shrinking files, you save space on devices and cloud services, cut costs on subscriptions or hardware, and make backups and transfers faster.
Whether you’re a student managing photos, a business owner handling client data, or anyone in between, compression helps you get more from your storage budget. Tools like 7-Zip, WinZip, or built-in features make starting easy. For added protection, combine compression with cloud backup.



