A well-thought-out backup retention policy ensures your data is available when needed while managing storage costs and compliance requirements. Organisations risk data loss, excessive storage costs, or non-compliance with regulatory standards without a structured policy.
Additionally, a well-defined retention policy helps in disaster recovery planning by ensuring critical data can be restored quickly in case of system failures or cyberattacks. It also aids in maintaining data integrity and supports legal and audit requirements by retaining necessary records for the required duration. Regularly reviewing and updating the policy ensures it remains effective and aligned with the organisation’s evolving needs.
Why is Backup Retention Important?
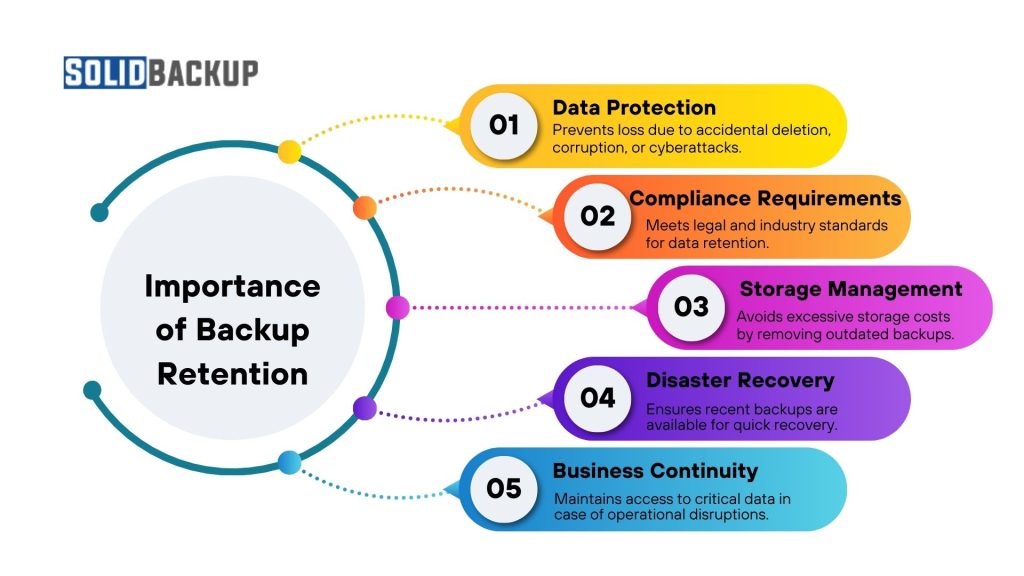
A proper backup retention strategy ensures that data remains accessible and secure while controlling storage costs. Back-up retention is crucial for organisations:
- Data Protection – Prevents loss due to accidental deletion, corruption, or cyberattacks.
- Compliance Requirements – Meets legal and industry standards for data retention.
- Storage Management – Avoids excessive storage costs by removing outdated backups.
- Disaster Recovery – Ensures recent backups are available for quick recovery.
- Business Continuity – Maintains access to critical data in case of operational disruptions.
Understanding Different Backup Retention Strategies
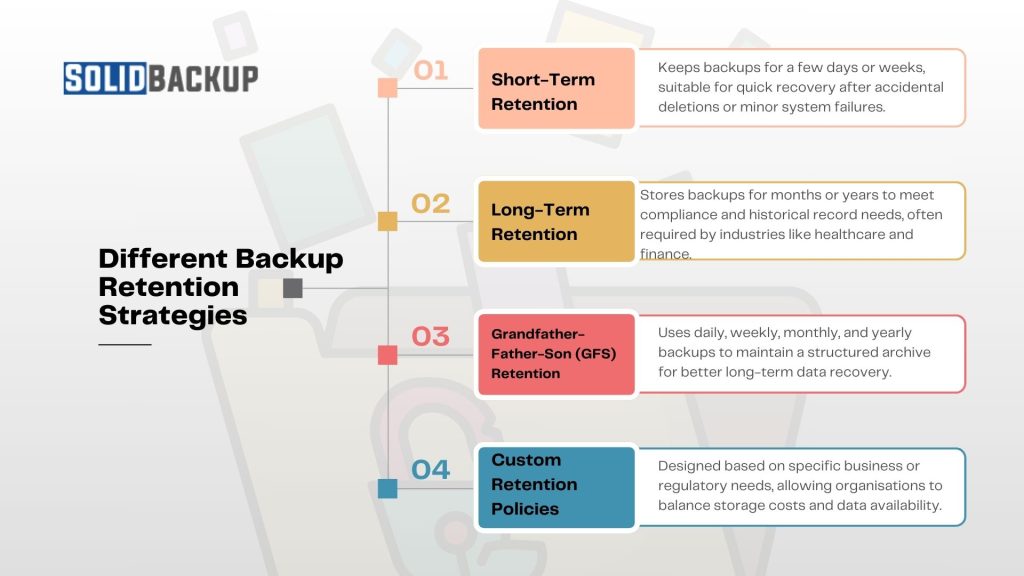
A well-planned backup retention strategy ensures efficient data storage and retrieval. Below are some common strategies:
- Short-Term Retention – Keeps backups for a few days or weeks, suitable for quick recovery after accidental deletions or minor system failures.
- Long-Term Retention – Stores backups for months or years to meet compliance and historical record needs, often required by industries like healthcare and finance.
- Grandfather-Father-Son (GFS) Retention – Uses daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly backups to maintain a structured archive for better long-term data recovery.
- Custom Retention Policies – Designed based on specific business or regulatory needs, allowing organisations to balance storage costs and data availability.
How to Create an Effective Backup Retention Policy
A strong backup retention policy ensures that critical data is available when needed while managing storage costs and compliance requirements. Following a structured approach, organisations can define clear retention periods, automate backups, and maintain secure, efficient data protection.
Here are the key steps to creating an effective policy:
- Assess Business Needs – Identify the criticality of different data types and the required retention period.
- Understand Compliance Laws – Ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX regulations, which mandate specific data retention periods.
- Classify Data – Segregate data into critical, essential, and non-essential categories for effective backup management.
- Choose a Backup Method – Based on storage capacity and recovery time objectives (RTOs), select between full, incremental, or differential backups.
- Define Retention Periods – Establish clear retention periods for daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly backups.
- Automate Backup Processes – Use backup software to schedule and enforce retention policies, reducing manual errors.
- Monitor and Audit – Regularly review backup policies, conduct tests, and adjust based on business growth and storage usage.
Key Considerations for Backup Retention Policy Implementation
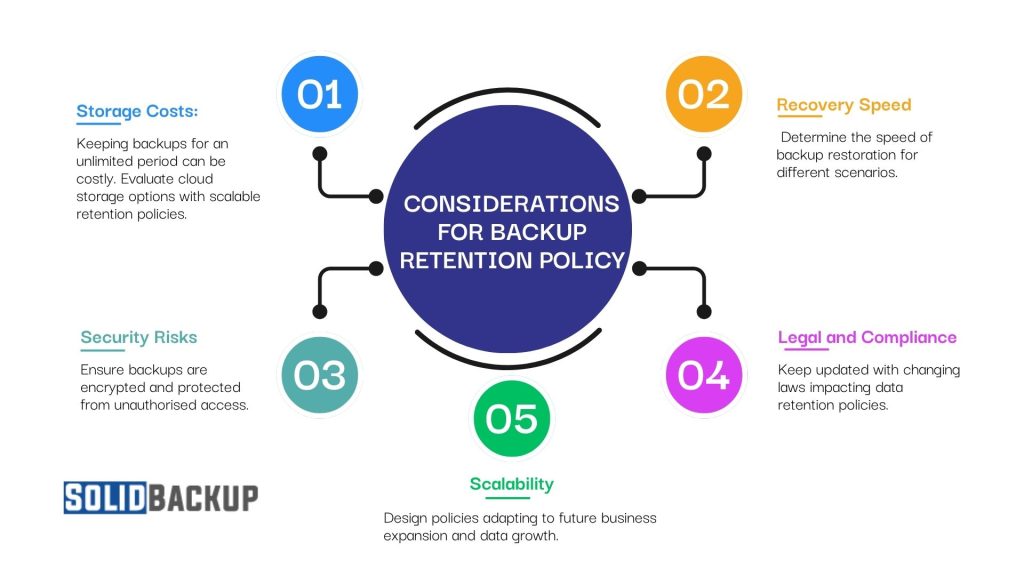
Implementing a backup retention policy requires careful planning to balance storage efficiency, security, and compliance. Consider these key factors to create an effective strategy:
- Storage Costs: Keeping backups for an unlimited period can be costly. Evaluate cloud storage options with scalable retention policies.
- Security Risks: Ensure backups are encrypted and protected from unauthorised access.
- Recovery Speed: Determine the speed of backup restoration for different scenarios.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Keep updated with changing laws impacting data retention policies.
- Scalability: Design policies adapting to future business expansion and data growth.
Best Practices for Backup Retention
Following industry best practices ensures an efficient and secure backup retention strategy. Implement these key recommendations to optimise data protection.
Implementing best practices for backup retention is crucial for ensuring data security, compliance, and cost management. Here are some key practices to consider:
- Scalability: Design policies adapting to future business expansion and data growth.
- Classify Data by Type and Needs: Identify and categorise data based on its importance and usage. This helps determine the appropriate retention period for different types of data.
- Categorise Data by Lifecycle: Understand the lifecycle of your data, from creation to deletion. This helps in planning retention policies that align with business processes and compliance requirements.
- Define Retention Periods: Set clear retention periods for different types of data. Consider legal, regulatory, and business needs when defining these periods.
- Version Control: Decide on the number and type of versions to store. Keeping multiple versions can help in recovering from accidental deletions or corruption.
- Backup Frequency: Determine the frequency of backups based on the criticality of the data. More frequent backups may be necessary for mission-critical data.
- Compliance and Security: Ensure your backup strategy complies with relevant regulations and standards. Implement security measures to protect backup data from unauthorised access.
- Cost Management: Choose cost-effective backup solutions that meet your needs without overspending. Review and optimize your storage usage regularly to manage costs effectively.
- Regular Reviews: Review and update your backup retention policy to ensure it remains effective and aligned with evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Best Practices for Maintaining Backup Data Durability
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule – Keep three copies of data on two different media, with one offsite.
- Use Cloud Backup Services – Cloud storage provides scalable and secure retention.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data – Protect backups with strong encryption to prevent unauthorised access.
- Test Backup Restores – Ensure backups function correctly and you can restore them when needed.
- Review Policies Periodically – Adjust retention periods based on evolving business needs and storage costs.
- Implement Versioning – Maintain multiple versions of files to recover from accidental changes or corruption.
- Set Automated Deletion Policies – Prevent unnecessary storage costs by removing outdated backups automatically.
Recommended Cloud Backup Solutions
Cloud storage services offer flexible and automated backup retention policies. Some of the best options include:
- Microsoft OneDrive – Ideal for small businesses and personal use with built-in versioning and file recovery options.
- Google Drive – Provides automatic cloud backups and easy file access across devices.
- Amazon S3 Glacier – Suitable for long-term archival storage with cost-effective retention policies.
- Backblaze B2 – Affordable cloud storage with easy integration for automated backup management.
- Acronis Cyber Protect – Offers advanced security features along with cloud backup solutions.
Common Mistakes in Backup Retention and How to Avoid Them
Many businesses make critical errors in backup retention, leading to data loss or inefficiencies. Avoid these common mistakes to ensure a robust backup strategy:
- Retaining Data for Too Long – Holding onto unnecessary backups increases storage costs. Define clear deletion policies.
- Not Keeping Multiple Copies – Relying on a single backup increases the risk of data loss. Use multiple storage locations.
- Ignoring Security Measures – Failing to encrypt backups can expose sensitive data to cyber threats.
- Not Testing Restores – Backups serve no purpose if you cannot restore them. Conduct regular restoration tests.
- Lack of Documentation – Documenting retention policies helps ensure consistency and compliance.
Future Trends in Backup Retention
As technology evolves, so do backup retention strategies. Emerging innovations like AI, blockchain, and hybrid cloud solutions are shaping the future of data protection. Here are some key trends influencing backup retention:
- AI-Based Backup Management – AI helps optimise retention policies by predicting storage needs.
- Blockchain for Data Integrity – Ensures secure and tamper-proof backup records.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions – Combining on-premises and cloud storage for cost-effective retention.
- Automated Compliance Audits – Backup solutions with built-in compliance checks simplify regulatory adherence.
Restoring from a backup is often faster than decrypting files using third-party tools or dealing with ransom payments. Automated backup scheduling keeps files continuously protected, reducing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Conclusion
A well-structured backup retention policy helps businesses maintain data integrity, comply with regulations, and optimise storage use. Implementing best practices and leveraging cloud backup solutions ensures a reliable and efficient data protection strategy. Regularly reviewing and updating policies ensures they remain effective as technology and business needs evolve.



